Personal Safety and Process Safety
7 Key Differences Between Personal Safety and Process Safety
When it comes to workplace safety, people often assume that all safety efforts are the same. But in reality, there are different areas of safety management that serve distinct purposes. Two of the most important concepts are personal safety and process safety. While both aim to prevent harm, they focus on different aspects of risk and protection. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for ensuring a safe and well-managed work environment.
Let’s dive into the seven key differences between personal safety and process safety to help you better understand their unique roles.
1. Focus Area: Individual vs. System-Wide Protection
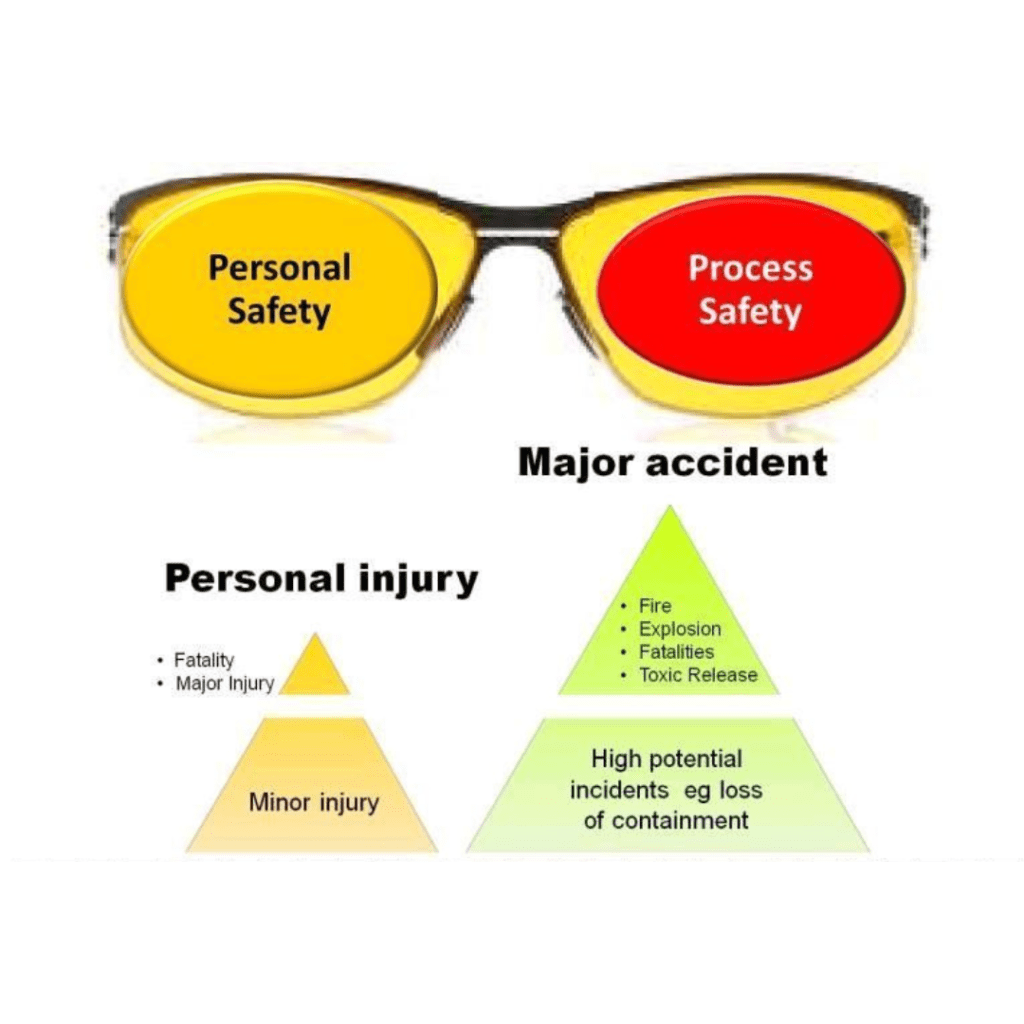
- Personal Safety: Focuses on the safety of individuals, ensuring that workers are protected from day-to-day hazards such as slips, trips, or falling objects.
- Process Safety: Deals with managing complex systems and processes to prevent large-scale accidents like chemical spills, fires, or explosions.
While personal safety ensures that employees are safe on a day-to-day basis, process safety aims to prevent catastrophic events that could impact both people and infrastructure.
2. Types of Risks Addressed
- Personal Safety: Focuses on risks that arise from everyday activities, such as not wearing protective gear or unsafe lifting techniques.
- Process Safety: Addresses risks associated with equipment failure, chemical reactions, or system malfunctions that could cause widespread harm.
For example, personal safety tackles things like using gloves to prevent hand injuries, while process safety manages risks like ensuring a chemical plant doesn’t overheat and explode.
3. Timeframe of Incidents
- Personal Safety: Deals with immediate risks, such as injuries that can occur in an instant—like falling from a ladder.
- Process Safety: Focuses on long-term risks that develop over time, often due to poor maintenance, design flaws, or operational errors.
Process safety incidents often take time to build up, but when they occur, the consequences are severe. Think of it like a pressure cooker—if maintained properly, it’s safe. But one unnoticed problem can result in an explosion.
4. Scale of Impact
- Personal Safety: Typically affects one or a few individuals at a time, such as a worker spraining an ankle.
- Process Safety: Can impact entire plants, communities, or ecosystems, like an oil refinery explosion that causes widespread damage and environmental harm.
While personal safety incidents are serious, process safety failures can have devastating, large-scale consequences.
5. Prevention Methods
- Personal Safety: Prevention focuses on training, personal protective equipment (PPE), and following safety protocols to reduce common accidents.
- Process Safety: Requires engineering controls, system inspections, and risk assessments to prevent failures in systems and equipment.
For instance, personal safety training teaches workers how to wear safety harnesses properly, while process safety involves installing pressure relief valves to prevent machinery from overheating.
6. Measurement of Safety Performance
- Personal Safety: Performance is often measured by injury rates, near-miss reports, and the number of safety violations.
- Process Safety: Uses indicators like system downtime, equipment reliability, and incident severity to assess safety levels.
Personal safety metrics track the frequency of smaller, individual accidents, while process safety looks at the health of entire systems to predict and prevent larger failures.
7. Response to Incidents
- Personal Safety: Involves immediate first aid or medical attention to treat injuries, followed by investigations to prevent similar accidents.
- Process Safety: Requires a comprehensive emergency response plan, including fire suppression systems, evacuation procedures, and environmental containment strategies.
For example, if a worker cuts their hand, personal safety protocols involve first aid and reporting the incident. In process safety, if a toxic gas leak occurs, emergency protocols are activated to contain the leak and protect nearby areas.
Conclusion
Both personal safety and process safety play crucial roles in keeping workplaces safe. While personal safety focuses on protecting individuals from immediate risks, process safety aims to prevent large-scale disasters that could affect many people and systems. It’s important for companies to address both aspects to create a safe, efficient, and sustainable work environment. At Ability Trading LLC, we understand the importance of both personal and process safety. That’s why we provide high-quality safety equipment and solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of each type of safety management. Whether you need PPE to protect individual workers or reliable systems to prevent large-scale incidents, Ability Trading LLC has you covered. Safety isn’t just a priority—it’s our commitment.

